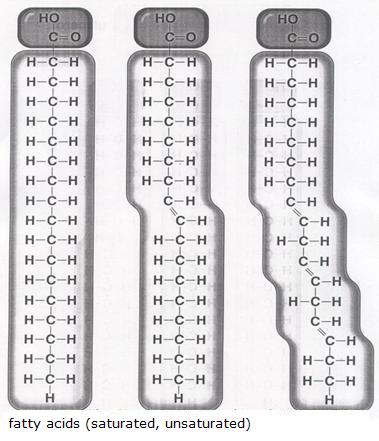
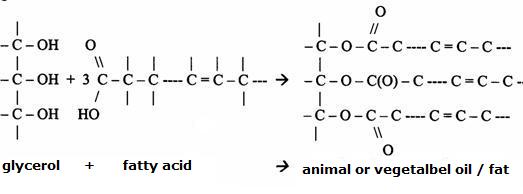
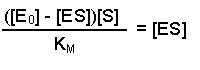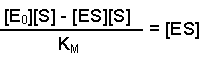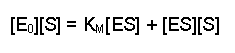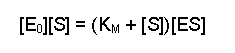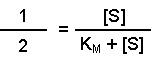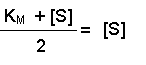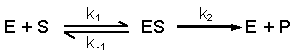|
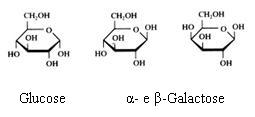
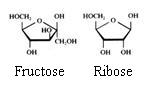
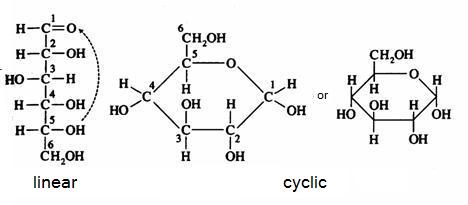
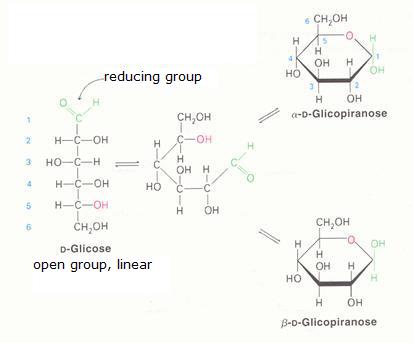
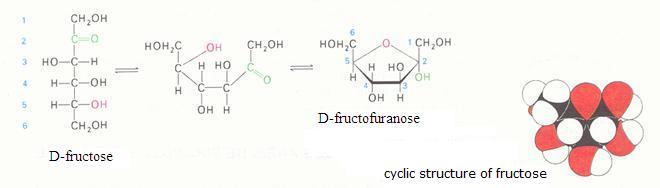
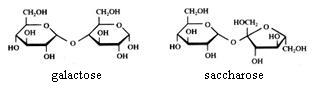
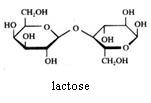
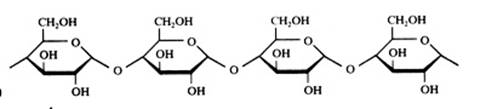
2. Carbohydrates / Saccharides / 2.1 Structures of carbohydrates |
|
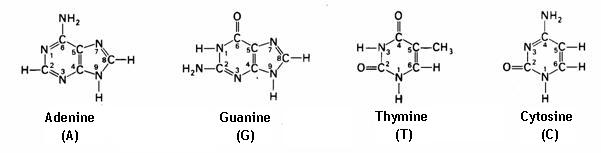
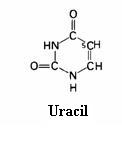
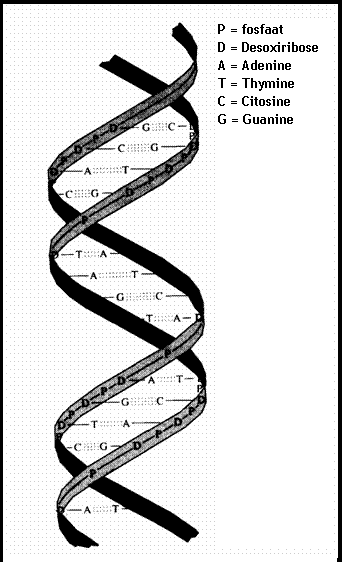
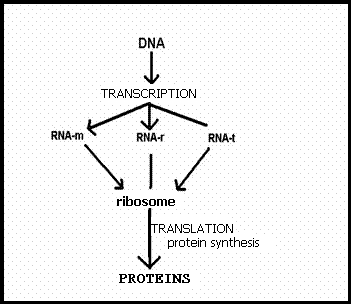
4.1 The basis of nucleic acids / the building bricks of life |
|
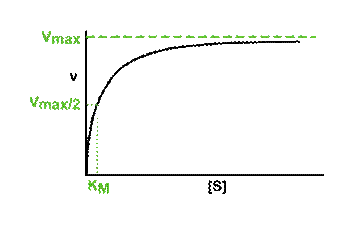
5.3 Optimal activity and denaturation of enzymes |
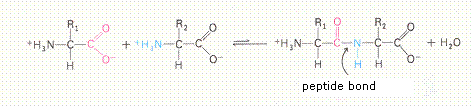
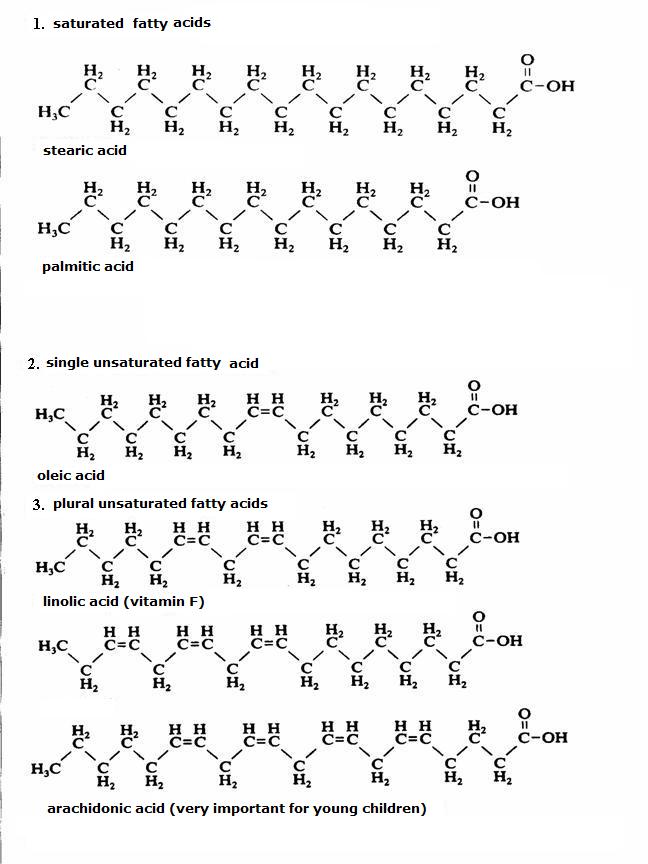
| amino acids serve to produce fats; | T / F |
| There are ten for human essential amino acids; | T / F |
| All amino acids have an amphoteric character. | T / F |


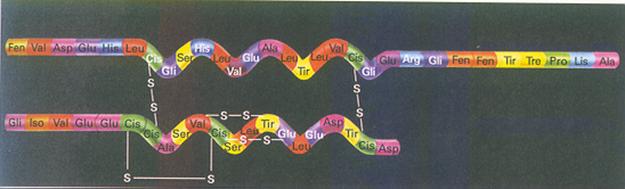
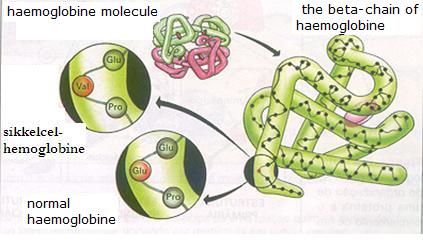
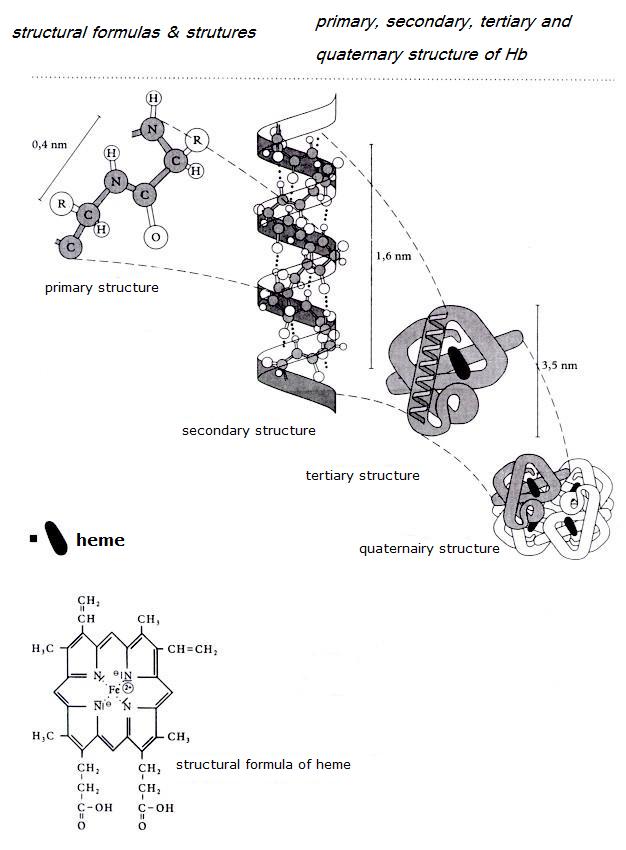
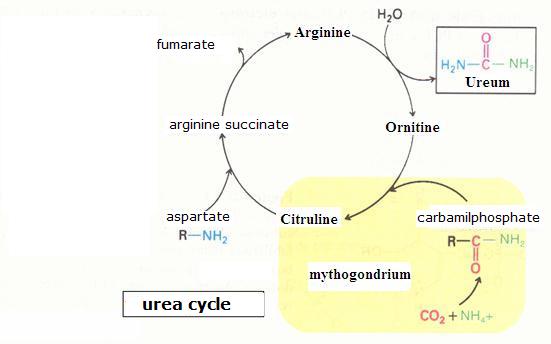

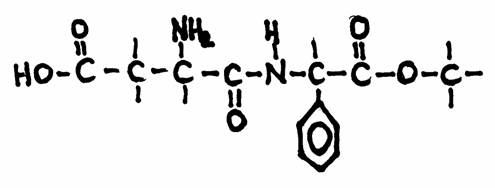
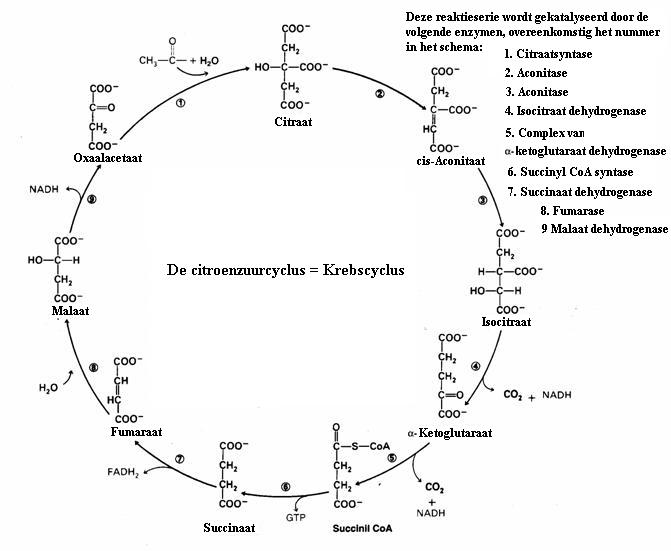
| Citrate |
|
oxalic acetate | |||
| C6H5O72- | + | H2O |
|
C4H2O52- | + 2CO2 + 5H· |


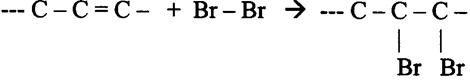

| Oxyreductases | catalyse redox reactions (for example: glucose-oxidase) |
| Transferases | transport functional groups of a donator to a receiver |
| Hydrolases | split molecules (for example: peptidases, proteases) |
| Liases | distract or add: certain functional groups (for example: decarboxylase) |
| Isomerases | change isomeres (mutase) |
| Ligases | connect different molecules with each other (piruvaate carboxylase) |
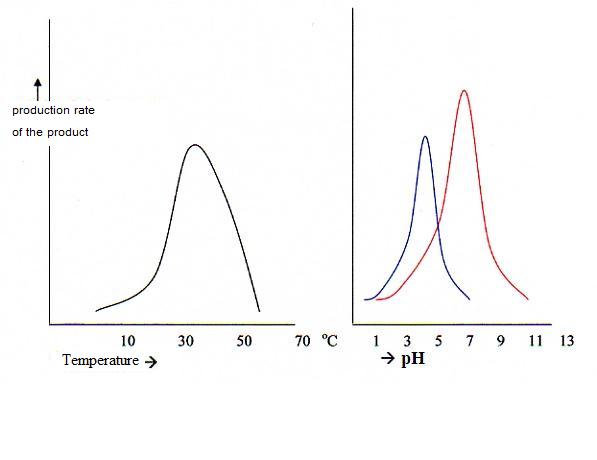
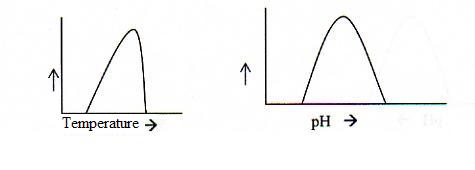
| Pepsine | 1,5 | in the stomach |
| Amilase | 6,6 | in saliva |
| Lipase | 8,0 resp. 7,0 | in the pancreas and in the bowels |
| Saccharase | 7,0 | in the stomach |
| place | enzimes | pH-optimum |
| In saliva | amilase and maltase | 6,6 |
| In the stomach | peptase, rennase | 1,5 - 4 |
| In the pancreas | amilase, maltase, lipase, tryptase, polipeptidase | 6,6 - 9 |
| In the bowels | maltase, saccharase, lactase, ereptase | 6,6 – 8,5 |
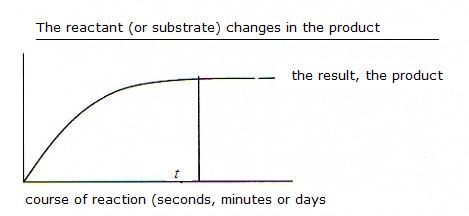


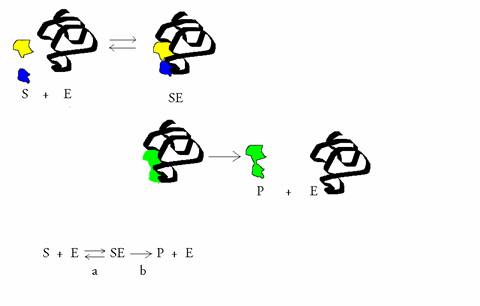



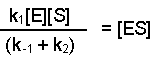
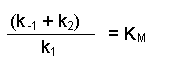
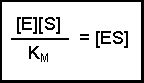 (Equation 2)
(Equation 2)