| CHEMISTRY
Answers Glossary Tables | MODULES:
01: Atoms 02: Periodic Table / Elements 03: Chemical Bonds 04: Nomenclature 05: Structures of Matter 06: Substances of the environment 07: Chemical Reactions 08: Reactions in Equilibrium 09: Acid-base-reactions 10:Redox reactions 11: Carbon chemistry 12: Biochemistry 13: Qualitative analysis 14: Quantitative analysis 15: Chemical Industry 16: Reactions in the environment |
TABLES FOR CHEMISTRY
Content:III. Composition of human body
IV. Distances between atoms, in 10-10 M
V. The elements and some properties
IX. Nomenclature in Carbon chemistry
XI. Solubility of salts in water
XV. Periodic Table, main groups only
I. Acids and conjugated bases
| ACID | Ka | pKa | BASE | Kb | pKb | |
| HClO4 | >>>1 | <<0 | ClO4- | <<<1 | >>14 | |
| HI | >>>1 | <<0 | I- | <<<1 | >>14 | |
| HBr | >>>1 | <<0 | Br- | <<<1 | >>14 | |
| HCl | >>>1 | <<0 | Cl- | <<<1 | >>14 | |
| H2SO4 | >>>1 | <<0 | HSO4- | <<<1 | >>14 | |
| HNO3 | >>>1 | <<0 | NO3- | <<<1 | >>14 | |
| HClO3 | >>>1 | <<0 | ClO3- | <<<1 | >>14 | |
| H3O+ | ±55.6 | ±1.75 | H2O | ±0.02 x 10-14 | ±15.75 | |
| (H2SO3) | 10-2 | ±2 | HSO3- | ±10-12 | ±12 | |
| HSO4- | 10-2 | ±2 | SO42- | ±10-12 | ±12 | |
| H3PO4 | 10-2 | ±2 | H2PO4- | ±10-12 | ±12 | |
| HF | 10-3 | ±3 | F- | ±10-11 | ±11 | |
| HCOOH | 10-4 | ±4 | HCOO- | ±10-10 | ±10 | |
| CH3COOH | 10-4 | ±4 | CH3COO- | ±10-10 | ±10 | |
| Al(H2O)63+ | 10-5 | ±5 | Al(OH)(H2O)52+ | ±10-9 | ±9 | |
| (H2CO3) | 10-6 | ±6 | HCO3- | ±10-8 | ±8 | |
| H2S | 10-7 | ±7 | HS- | ±10-7 | ±7 | |
| H2PO4- | 10-7 | ±7 | HPO42- | ±10-7 | ±7 | |
| HSO3- | 10-8 | ±8 | SO32- | ±10-6 | ±6 | |
| NH4+ | 10-10 | ±10 | NH3 | ±10-4 | ±4 | |
| HCO3- | 10-10 | ±10 | CO32- | ±10-4 | ±4 | |
| HPO42- | 10-13 | ±13 | PO43- | ±10-1 | ±1 | |
| HS- | 10-13 | ±13 | S2- | ±10-1 | ±1 | |
| H2O | ±0.02 x 10-14 | ±15.75 | OH- | ±55,6 | ±1.75 | |
| the lower in this table, | the weaker the acid | the lower in this table, | the stronger the base |
Strong acids have weak conjugated bases, en vice versa
The values of K and pK are rounded.
II. The Greek alphabeth
Greek letters (capitals and small) often are used as symbols in science.A a |
alfa | B b |
beta | Dd |
delta | E e |
epsilon | |||
| G g |
gama | C c |
chis | F j |
fi | H h |
eta | |||
| I i |
iota | K k |
kapa | L l |
lambda | M m |
mi | |||
| N n |
ni | O o |
omicron | P p |
pi | Q q |
teta | |||
| R r |
rho | S s |
sigma | T t |
tau | U u |
upsilon | |||
| W w |
omega | X x |
csi | Y y |
psi | Z z |
zeta |
III. Composition of human body
| Water: | H2O | ± 60% |
| Other materials: | H | 3% |
| C | 20 % | |
| O | ± 9 % | |
| N | ± 3 % | |
| Ca | ± 2,5 % | |
| P | ± 1,1 % | |
| Other elements | ± <1 % |
IV. Bonding distances between atoms, in 10-10 M
H-H |
0,74 | H-F |
0,92 | N≡N |
1,10 | C-F |
1,38 |
F-F |
1,42 | H-Cl |
1,27 | C≡C |
1,21 | C-Cl |
1,77 |
Cl-Cl |
1,99 | H-Br |
1,41 | C≡N |
1,16 | C-Br |
1,94 |
Br-Br |
2,28 | H-I |
1,60 | C=O (CO2) |
1,16 | C-I |
2,14 |
I-I |
2,67 | H-O |
0,96 | C=O |
1,22 | C-O |
1,43 |
N-N |
1,47 | N-H |
1,01 | C=C |
1,35 | H-S |
1,34 |
C-C |
1,54 | C-H |
1,08 | O=O |
1,21 | P-H |
1,42 |
V. The elements and some properties
| 1 = elements |
2 = symbol |
3 = atom- number |
4 = atom- mass |
5 = electro negati vity |
6 = melting- point |
7 = boiling- point |
8 = atom- ray x 10-12m |
9 = ion- ray x 10-12m |
10 = v-d-Waals ray x 10-12m |
| Actinium | Ac | 89 | 1,1 | 1324 | 3500 | 188 | |||
| Aluminum | Al | 13 | 27 | 1,6 | 933 | 2792 | 143 | 45 | |
| Americium | Am | 95 | 1,3 | 1400 | 2900 | 173 | |||
| Antimony | Sb | 51 | 121,8 | 2,1 | 904 | 1860 | 141 | 245 | 220 |
| Argon | Ar | 18 | 39,9 | 84 | 87 | 192 | |||
| Arsenic | As | 33 | 74,9 | 2,2 | 1090 | 887 | 121 | 222 | 200 |
| Astatin | At | 85 | 2,2 | 575 | 610 | 140 | |||
| Barium | Ba | 56 | 137,3 | 0,9 | 1000 | 2170 | 217 | 134 | |
| Beryllium | Be | 4 | 9,0 | 1,6 | 1560 | 2744 | 112 | 30 | |
| Berkelium | Bk | 97 | 1,3 | 1300 | 2900 | 172 | |||
| Bismuth | Bi | 83 | 209,0 | 2,0 | 545 | 1837 | 170 | ||
| Boron | B | 5 | 10,8 | 2,0 | 2348 | 4273 | 88 | 16 | 217 |
| Bromine | Br | 35 | 79,9 | 3,0 | 266 | 332 | 114 | 196 | 195 |
| Cadmium | Cd | 48 | 112,4 | 1,7 | 594 | 1040 | 149 | 97 | |
| Calcium | Ca | 20 | 40,1 | 1,0 | 1115 | 1757 | 197 | 94 | |
| Californium | Cf | 98 | 1,3 | 1200 | 1700 | 199 | |||
| Carbon | C | 6 | 12,0 | 2,6 | 3823 | 4098 | 77 | 185 | |
| Cerium | Ce | 58 | 140,1 | 1,1 | 1070 | 3698 | 183 | 101 | |
| Cesium | Cs | 55 | 132,9 | 0,9 | 302 | 944 | 262 | 167 | |
| Chromium | Cr | 24 | 52,0 | 1,6 | 2180 | 2944 | 125 | 63 | |
| Chlorine | Cl | 17 | 35,5 | 3,2 | 172 | 239 | 99 | 181 | 180 |
| Cobalt | Co | 27 | 58,9 | 1,7 | 1968 | 3200 | 125 | 74 | |
| Copper | Cu | 29 | 63,5 | 1,8 | 1357 | 2835 | |||
| Curium | Cm | 96 | 1600 | 3400 | 174 | ||||
| Dysprosium | Dy | 66 | 162,5 | 1,2 | 1681 | 2835 | 175 | ||
| Einsteinium | Es | 99 | 1100 | 1800 | 203 | ||||
| Erbium | Er | 68 | 167,3 | 1802 | 3136 | 173 | |||
| Europium | Eu | 63 | 152,0 | 1099 | 1875 | 204 | |||
| Fluorin | F | 9 | 19,0 | 4,0 | 54 | 85 | 64 | 133 | 135 |
| Francium | Fr | 87 | 0,9 | 300 | 950 | 270 | 180 | ||
| Gadolinium | Gd | 64 | 157,3 | 1,1 | 1585 | 3534 | 179 | ||
| Gallium | Ga | 31 | 69,7 | 1,8 | 303 | 2477 | 141 | ||
| Germanium | Ge | 32 | 72,6 | 2,0 | 1211 | 3106 | 122 | 202 | |
| Gold (Aurum) | Au | 79 | 197,0 | 1,4 | 1337 | 3129 | 144 | 137 | |
| Hafnium | Hf | 72 | 178,5 | 1,2 | 2506 | 4876 | 144 | ||
| Helium | He | 2 | 4,0 | 2 | 4 | 157 | 99 | ||
| Hydrogen | H | 1 | 1,0 | 2,2 | 14 | 20 | 30 | 120 | |
| Holmium | Ho | 67 | 164,9 | 1,2 | 1738 | 2968 | 174 | ||
| Indium | In | 49 | 114,8 | 1,5 | 430 | 2345 | 166 | ||
| Iodine | I | 53 | 126,9 | 2,7 | 387 | 458 | 133 | 219 | 215 |
| Iridium | Ir | 77 | 192,2 | 1,6 | 2719 | 4701 | 135 | ||
| Iron (Ferrum) | Fe | 26 | 55,8 | 1,6 | 1811 | 3134 | 126 | 76 | |
| Krypton | Kr | 36 | 83,8 | 116 | 120 | 197 | |||
| Lantanium | La | 57 | 138,9 | 1,1 | 1193 | 3728 | 188 | ||
| Lead | Pb | 82 | 207,5 | 1,6 | 601 | 2022 | 175 | 120 | |
| Lithium | Li | 3 | 6,9 | 1,0 | 454 | 1615 | 152 | 68 | |
| Lutetium | Lu | 71 | 175,0 | 1,2 | 1928 | 3668 | 172 | ||
| Magnesium | Mg | 12 | 24,3 | 1,2 | 923 | 1363 | 160 | 65 | |
| Manganese | Mn | 25 | 54,9 | 1,6 | 1915 | 2334 | 129 | 80 | |
| Mercury | Hg | 80 | 200,6 | 1,4 | 234 | 630 | 152 | 127 | |
| Molybdenium | Mo | 42 | 95,9 | 1,3 | 2856 | 4912 | 136 | ||
| Neodymium | Nd | 60 | 144,2 | 1,2 | 1293 | 3300 | 181 | ||
| Neon | Ne | 10 | 20,2 | 25 | 27 | 160 | |||
| Niobium | Nb | 41 | 92,9 | 1,2 | 2750 | 5017 | 141 | ||
| Nickel | Ni | 28 | 58,7 | 1,8 | 1728 | 3186 | 124 | 72 | |
| Nitrogen | N | 7 | 14,0 | 3,0 | 63 | 77 | 70 | 171 | 150 |
| Osmium | Os | 76 | 190,2 | 1,5 | 1828 | 3236 | 134 | ||
| Oxigen | O | 8 | 16,0 | 3,4 | 54 | 90 | 66 | 146 | 140 |
| Palladium | Pd | 46 | 106,4 | 1,4 | 1828 | 3236 | 138 | ||
| Phosphorus | P | 15 | 31,0 | 2,1 | 317 | 550 | 110 | 212 | 190 |
| Platinum | Pt | 78 | 195,1 | 1,4 | 2042 | 4098 | 138 | ||
| Plutonium | Pu | 94 | 910 | 3600 | 159 | ||||
| Polonium | Po | 84 | 1,8 | 527 | 1235 | 140 | |||
| Potassium | K | 19 | 39,1 | 0,8 | 336 | 1032 | 231 | 133 | |
| Praseodimium | Pr | 59 | 140,9 | 1,2 | 1208 | 3785 | 182 | ||
| Promethium | Pm | 61 | 1,2 | 1341 | 3003 | 183 | |||
| Protactinium | Pa | 91 | 1,5 | 1800 | 4400 | 156 | |||
| Radium | Ra | 88 | 0,9 | 972 | 1413 | 220 | 148 | ||
| Radon | Rn | 86 | 202 | 211 | |||||
| Rhenium | Re | 75 | 186,2 | 1,9 | 3459 | 5869 | 137 | ||
| Rhodium | Rh | 45 | 102,9 | 2,3 | 2237 | 2968 | 134 | ||
| Rubidium | Rb | 37 | 85,5 | 0,8 | 312 | 961 | 244 | 148 | |
| Ruthenium | Ru | 44 | 101,1 | 2,2 | 2607 | 4423 | 133 | ||
| Samarium | Sm | 62 | 150,4 | 1,2 | 1345 | 2064 | 180 | ||
| Scandium | Sc | 21 | 45,0 | 1,2 | 1814 | 3195 | 160 | ||
| Selenium | Se | 34 | 79,0 | 2,6 | 494 | 958 | 117 | 202 | 200 |
| Silicon | Si | 14 | 28,1 | 1,9 | 1687 | 3538 | 117 | 224 | |
| Silver | Ag | 47 | 107,9 | 1,9 | 1235 | 2435 | 144 | 126 | |
| Sodium | Na | 11 | 23,0 | 0,9 | 371 | 1156 | 186 | 98 | |
| Strontium | Sr | 38 | 87,6 | 1,0 | 1050 | 1655 | 215 | 110 | |
| Sulphur | S | 16 | 32,1 | 2,5 | 388 | 718 | 104 | 190 | 185 |
| Tantalium | Ta | 73 | 180,9 | 1,3 | 3269 | 5731 | 143 | ||
| Thallium | Tl | 81 | 204,4 | 2,0 | 577 | 1746 | 171 | ||
| Technetium | Tc | 43 | 1,9 | 2430 | 4538 | 135 | |||
| Tellurium | Te | 52 | 127,6 | 2,1 | 723 | 1261 | 137 | 222 | 220 |
| Terbium | Tb | 65 | 158,9 | 1,2 | 1629 | 3396 | 167 | ||
| Tin (Stannium) | Sn | 50 | 118,7 | 1,7 | 505 | 2875 | 162 | 112 | |
| Titanium | Ti | 22 | 47,9 | 1,5 | 1941 | 3560 | 146 | 90 | |
| Thorium | Th | 90 | 232,0 | 1,3 | 2000 | 4800 | 180 | ||
| Thullium | Tm | 69 | 168,9 | 1,2 | 1818 | 2221 | 172 | ||
| Uranium | U | 92 | 238,0 | 1,4 | 1400 | 4200 | 138 | ||
| Vanadium | V | 23 | 50,9 | 1,6 | 2183 | 3680 | 131 | ||
| Tungsten (Wolfframium) | W | 74 | 183,9 | 2,4 | 3695 | 5828 | 137 | ||
| Xenon | Xe | 54 | 131,3 | 161 | 165 | 217 | |||
| Ytterbium | Yb | 70 | 173,0 | 1,1 | 1097 | 1467 | 194 | ||
| Yttrium | Y | 39 | 88,9 | 1,1 | 1799 | 3609 | 180 | ||
| Zinc | Zn | 30 | 65,4 | 1,7 | 693 | 1180 | 133 | 74 | |
| Zirconium | Zr | 40 | 91,2 | 1,3 | 2128 | 4682 | 157 |
VI. BONDING ENERGIES
x 100 kJ/moleH-H |
- 4,36 | H-F |
- 5,63 | N≡N |
- 9,45 | C-F |
- 4,4 |
F-F |
- 1,53 | H-Cl |
- 4,32 | C≡C |
- 8,3 | C-Cl |
- 3,3 |
Cl-Cl |
- 2,43 | H-Br |
- 3,66 | C≡N |
- 8,9 | C-Br |
- 2,8 |
Br-Br |
- 1,93 | H-I |
- 2,99 | C=O |
- 8,0 | C-I |
- 2,4 |
I-I |
- 1,51 | H-O |
- 4,646 | C=S |
- 2,6 | C-O |
- 3,5 |
H-O (alcanol) |
- 4,5 | N-H |
- 3,9 | C=C |
- 6,1 | H-S |
- 3,44 |
C-C |
- 3,5 | C-H |
- 4,1 | O=O |
- 4,98 | P-H |
- 3,22 |
VII. PHASES
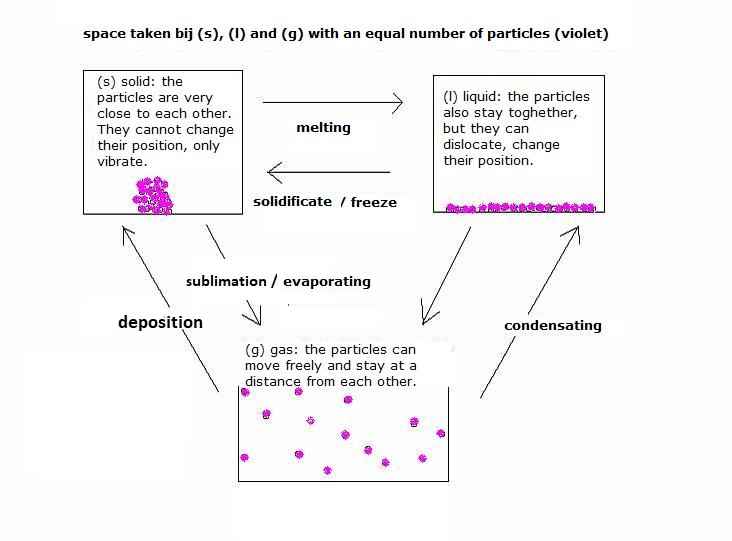
VIII. Indicators
| INDICATOR | colour at low pH | transition zone | colour at high pH |
| hematoxiline | red | 0,0 - 1,0 | yellow |
| cresolred | red | 0,2 - 1,8 | yellow |
| thymolblue | red | 1,2 - 2,8 | yellow |
| dimethylyellow | red | 2,9 - 4,0 | yellow |
| methylorange | red | 3,1 - 4,4 | orange-yellow |
| methylred | red | 4,0 - 6,0 | yellow |
| bromophenolred | yellow | 5,2 - 6,8 | violet |
| litmus | red | 5,5 - 8,0 | blue |
| bromothymolblue | yellow | 6,0 - 7,6 | blue |
| phenolred | yellow | 6,8 - 8,4 | red |
| thymolblue | yellow | 8,0 - 9,6 | blue |
| phenolftaleine | colourless | 8,2 - 10 | carminred |
| alizarine-R-yellow | yellow | 10,1 - 12 | violetblue |
| 1,3,5-trinitrobenzene | colourless | 12 - 14 | orange |
IX. NOMENCLATURE IN CARBONCHEMISTRY
| general name | general formula | remarks |
| Alkanes | CnH2n+2 | just single C-C bondsalleen in the molecules |
| Alkenes | CnH2n | double C=C bonds in the molecules |
| Alkynes | CnH2n-2 | threfold C≡C bond in the molecules |
| Cycloalkanes | CnH2n | |
| Benzene | C6H6 |
The main chain of the molecule:
- normally is the longist chain;
- contains a double or threefold bonding or the functional group (if present);
- has as a suffix: -ane, -ene, -yne enz.
- gives the molecule its main name, bases on de number of C-atoms in the main chain.
| Only 1 C-atom: | met... | six C-atoms: | hex..... | |
| Two C-atoms: | et..... | Seven C-atoms: | hept...... | |
| Three C-atoms: | prop..... | Eight C-atoms: | oct....... | |
| Four C-atoms: | but...... | Nine C-atoms: | non...... | |
| Five C-atoms: | pent....... | Ten C-atoms: | dec........ |
- Carbon side chains always have suffix -yl
- the number of side chains and of funcional groups are counted and named: Mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, etc.
- The molecule can contain primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary C-atoms.
| name | general formula |
suffix | example | comment / alternative |
| alkane | CnH2n+2 | -aan | 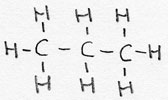
propane |
saturated |
| alkene | CnH2n | -ene | 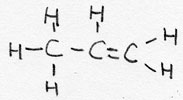 Propene |
unsaturated |
| Alkyne | CnH2n-2 | -yne | 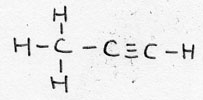
Propyne |
unsaturated |
| Alkyl- | CnH2n+1 -- | -yl |
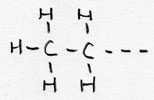
Ethyl--- |
side chaine/branche |
| cyclo-alkane | CnH2n | -ane |
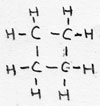
cyclo-butane |
isomer with alquenes/ saturated |
| alkanol | CnH2n+1 -OH | -ol |
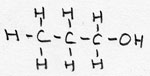
1-propanol |
prefix: hydroxy; / also called: alcohol |
| alkanal | CnH2n+1-CHO | -al |
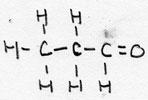
Propanal |
aldehyde |
| alkanone | CnH2n+1- -CO-CmH2m+1 |
-on |
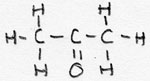
Propanone |
a ketongroup is present |
| alkanoic acid | CnH2n+1-COOH |
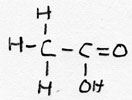
ethanoic acid |
acetic acid | |
| Alkoxy-alkane | CnH2n+1- O-
CmH2m+1 |
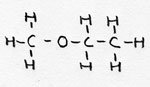
Methoxy-ethane |
Ether (2 alkylgroups connected via an O atom) | |
| Alkyl-alkan(o)ate | CnH2n+1-COO- /
CmH2m+1 |
-yl -oaat |
aat-.jpg)
Methyl-ethanoate |
an ester |
| Alkylamina (prim) | CnH2n+1-NH2 | -amina |
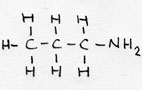
propyl-amina or: 1 aminopropane |
prefix: amino- |
| nitro-alkane | CnH2n+1-NO2 | 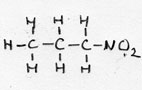
1-nitro propane |
prefix: nitro- | |
| peptide | CnH2n+1-NH-CO-CmH2m+1 |
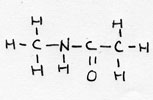 |
X. REDOX Half reactions
| oxydators | reductors | ||||||||||
| F2 | + | 2e- | 2F- | ||||||||
| H2O2 | + | 2H+ | + | 2e- | 2H2O | ||||||
| PbO2 | + | SO42 - | + | 4H+ | + | 2e- | PbSO4 | + | 2H2O | ||
| MnO4- | + | 8H+ | + | 5e- | Mn2+ | + | 4H2O | ||||
| Au3+ | + | 3e- | Au | ||||||||
| Cl2 | + | 2e- | 2Cl- | ||||||||
| Cr2O72- | + | 14H+ | + | 6e- | 2Cr3+ | + | 7H2O | ||||
| MnO2 | + | 4H+ | + | 2e- | Mn2+ | + | 2H2O | ||||
| O2 | + | 4H+ | + | 4e- | 2H2O | ||||||
| Br2 | + | 2e- | 2Br- | ||||||||
| NO3- | + | 2H+ | + | e- | NO2 | + | H2O | ||||
| Ag+ | + | e- | Ag | ||||||||
| Fe3+ | + | e- | Fe2+ | ||||||||
| I2 | + | 2e- | 2I- | ||||||||
| MnO4- | + | 2H2O | + | 3e- | MnO2 | + | 4OH- | ||||
| Cu2+ | + | 2e- | Cu | ||||||||
| Cu2+ | + | e- | Cu+ | ||||||||
| S | + | 2H+ | + | 2e- | H2S | ||||||
| S4O62- | + | 2e- | 2S2O32- | + | H2O | ||||||
| 2H+ | + | 2e- | H2 | ||||||||
| SO42- | + | 2H+ | + | 2e- | SO32- | + | H2O | ||||
| Pb2+ | + | 2e- | Pb | ||||||||
| Ni2+ | + | 2e- | Ni | ||||||||
| PbSO4 | + | 2e- | Pb | + | SO42- | ||||||
| Fe2+ | + | 2e- | Fe | ||||||||
| S | + | 2e- | S2- | ||||||||
| 2 CO2 | + | 2H+ | + | 2e- | H2C2O4 | ||||||
| Zn2+ | + | 2e- | Zn | ||||||||
| 2H2O | + | 2e- | H2 | + | 2OH- | ||||||
| Al3+ | + | 3e- | Al | ||||||||
| Mg2+ | + | 2e- | Mg | ||||||||
| Al(OH)4- | + | 3e- | Al | + | 4OH- | ||||||
| Na+ | + | e- | Na | ||||||||
| Ba2+ | + | 2e- | Ba | ||||||||
| Ca2+ | + | 2e- | Ca | ||||||||
| K+ | + | e- | K | ||||||||
| the lower, | the weaker the oxidator | the lower, | the stronger the reductor |
XI. SOLUBILITY OF SALTS IN WATER
| OH- | O2- | Cl- | Br- | I- | S2- | SO32- | SO42- | CO32- | PO43- | NO3- | CH3COO- | |
| Na+ | + |
R |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
| K+ | + |
R |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
| NH4+ | + |
+ |
+ |
D |
+ |
+ |
D |
D |
+ |
+ |
||
| Ca2+ | ± |
R |
+ |
+ |
+ |
± |
- |
± |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
| Ba2+ | + |
R |
+ |
+ |
+ |
± |
- |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
| Ag+ | - |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
± |
- |
- |
+ |
± |
|
| Pb2+ | - |
- |
± |
± |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
| Hg+ | - |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
± |
|
| Hg2+ | - |
+ |
± |
- |
- |
R |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
||
| Cu2+ | - |
- |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
+ |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
|
| Al3+ | - |
- |
+ |
+ |
+ |
R |
+ |
+ |
- |
+ |
+ |
|
| Fe2+ | - |
- |
+ |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
+ |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
| Fe3+ | - |
- |
+ |
+ |
- |
+ |
- |
+ |
+ |
|||
| Mg2+ | - |
- |
+ |
+ |
+ |
± |
- |
+ |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
| Zn2+ | - |
- |
+ |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
+ |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
| +: soluble | -: insoluble | ±: a bit soluble | R: reacts with water | D: decomposes int water |
just like salt with Sodium-, Potassium- or Ammonium-ions.
XII. DECIMAL PREFIXES
| Tera | T | 1012 | 1 000 000 000 000 | |
| Giga | G | 109 | 1 000 000 000 | |
| Mega | M | 106 | 1 000 000 | |
| Kilo | k | 103 | 1 000 | |
| Hecto | h | 102 | 100 | |
| Deca | da | 101 | 10 | |
| Deci | d | 10-1 | 0,1 | |
| Centi | c | 10-2 | 0,01 | |
| MiLli | m | 10-3 | 0,001 | |
| Micro | m | 10-6 | 0,000 001 | |
| Nano | n | 10-9 | 0,000 000 001 | |
| Pico | p | 10-12 | 0,000 000 000 001 |
XIII. DANGEROUS SUBSTANCES
- MAC: maximum allowable concentration, mg/m3
- General rule: consult a practitionar / hospital
- O: vomit
- W: drink or flush lots of water
- F: fresh air
name |
MAC value |
danger/div> |
toxicicity 1 - 5 |
do what? |
|||
acetilene |
ettyn |
H-C≡C-H |
g |
explosive |
1 |
WF / O |
|
Aceton |
propanon |
CH3COCH3 |
l |
1780 |
inflamable |
2 |
WF |
hydrocloric acid |
hydrogenchloride |
HCl (aq) |
aq |
7 |
itching |
2 |
W |
sulphuric acid |
H2SO4 |
1 |
aq |
itsching |
2 |
W |
|
alkohol |
ethanol |
CH3CH2OH |
1 |
1000 |
1 |
W |
|
ammonia |
NH3 |
g / aq |
18 |
dangerous vapor |
2 |
WF |
|
Arsenic + derivates |
As3+ |
s |
0,03 |
poisenous |
5 |
W |
|
benzene |
C6H6 |
1 |
7,5 |
WF |
|||
bromium |
Br2 |
l / aq |
0,7 |
carcinogenic suffocating |
2 |
O |
|
limestone |
calciumoxide |
CaO |
s |
5 |
1 |
W |
|
carbide |
calcium carbide |
C22- / CaC2 |
s |
explosive |
2 |
sand over it |
|
Lead and derivates |
Pb |
s |
0,15 |
poisonous |
4 |
W |
|
cyanides |
CN- |
s |
5 |
poisonous |
4 |
||
chlorine |
Cl |
g / aq |
3 |
poisonous |
4 |
WF |
|
chlorophorm |
trichloromethane |
CHCl3 |
1 |
5 |
dangerous vapors |
1 |
WF |
sulphurdioxyde |
SO2 |
g |
5 |
3 |
WF |
||
ether |
Ethoxi-ethane |
CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 |
1 |
1200 |
explosive |
1 |
WF |
phenol |
hydroxybenzene |
C6H5OH |
l |
19 |
itching |
2 |
|
fluorine |
F2 |
g |
2 |
poisonous |
4 |
||
phormalina |
Methanal |
CH2O |
l |
1,5 |
itching |
1 |
W |
petrol |
Octanes |
C8H18 |
l / g |
explosive |
1 |
WF |
|
glycol |
1.2 dihydroxy-ethane |
HO-CH2-CH2-OH |
l |
26 |
headache |
2 |
O |
Na/K hydroxide (aq) |
NaOH / KOH |
aq |
2 |
itching |
1 |
W |
|
Iodine |
I2 |
s |
1 |
headache |
2 |
W |
|
chlorine cleaning |
Sodium hypochlorite |
NaClO |
s / aq |
itching |
2 |
W |
|
mercury |
Hg / Hg2+ |
l |
0,05 |
poisonous |
5 |
W (milk) |
|
methylalcohol |
Methanol |
CH3OH |
l |
260 |
poisonous |
3 |
O |
carbon monoxyde |
CO |
g |
29 |
poisonous |
4 |
WF |
|
silver nitrate |
AgNO3 |
s |
0,01 |
itching |
W |
||
nitrogen oxydes |
NxOy (NO2 NO3 etc) |
g |
4 |
headache |
3 |
WF |
|
ozon |
O3 |
g |
poisonous |
3 |
WF |
||
hydrogen peroxyde |
H2O2 |
l |
1,4 |
burns skin/ explosive |
2 |
W |
|
Tetra |
tetracloromethane |
CCl4 |
l |
12,6 |
poisonous |
3 |